Production of pozzolana by flash calcination of natural clay soils
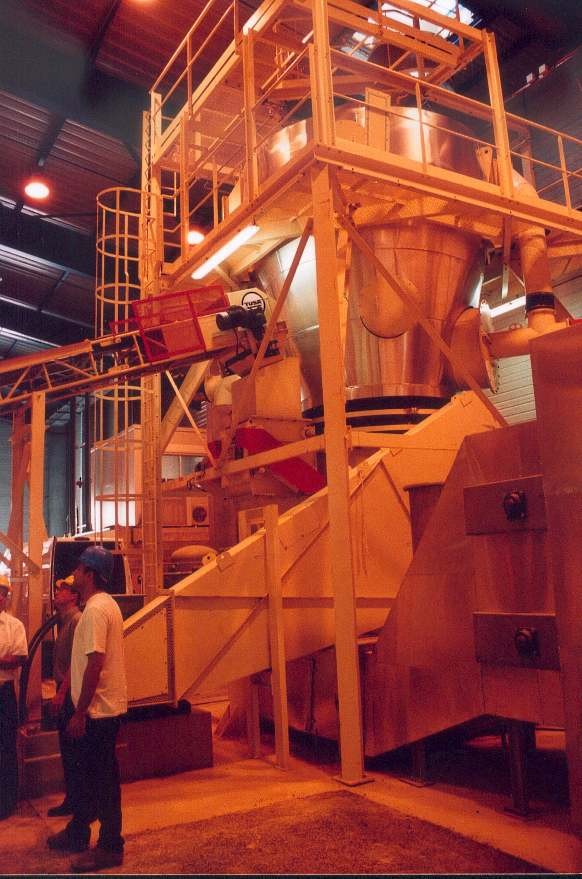
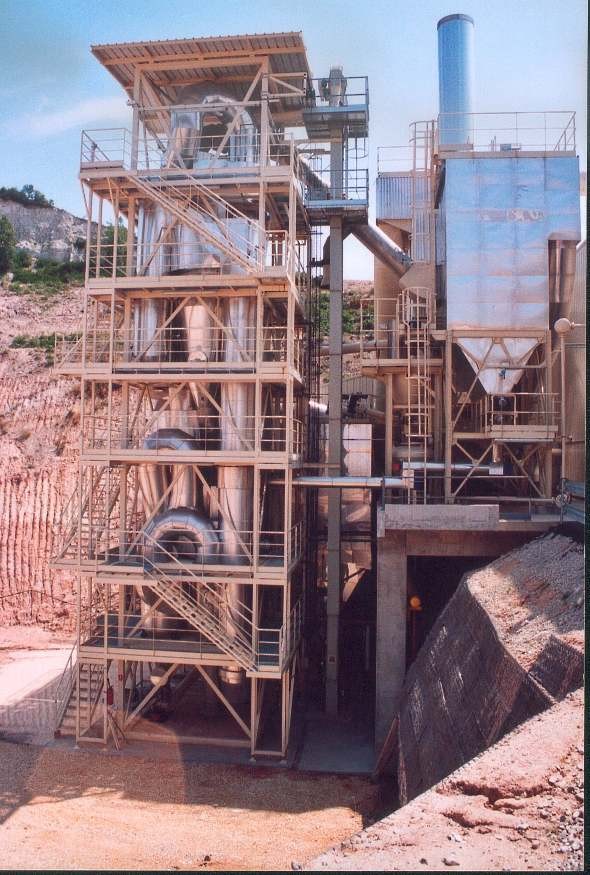
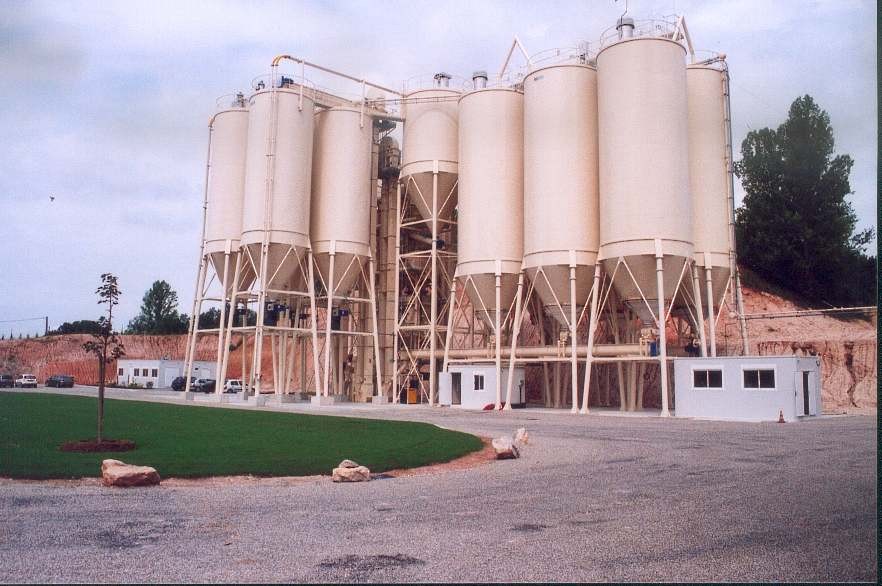
Hydraulic binders such as cement are used massively around the world. They are produced in very large scale plants, and their cost can become very high after delivering in isolated places or road-works. The aim of this project was to develop small scale and semi-mobile units to produce a binder locally. The binder is composed of calcined clay or clay soil added with lime.The flash calcination technique was first selected and validated, in the laboratory and based on a numerical model taking into account the particle size and the reaction temperature. A 500 kg/h pilot unit was then designed, constructed and successfully operated in Toulouse, France. A 10 t/h plant was then built in Fumel, France, and is still operated. A second plant - using solid fuels as the energy input - has been installed in Surinam.
It was shown that calcined clay - or metakaolin - can also be substituted to part of the cement in a concrete, with an increase of its long term performances.
Actions
Production of synthetic pozzolana by flash calcination of clay soils.
Production de pouzzolanes de synthèse par calcination flash de sols argileux ; étude des produits et conception d'une installation.
20 november 1992, INSA Toulouse.
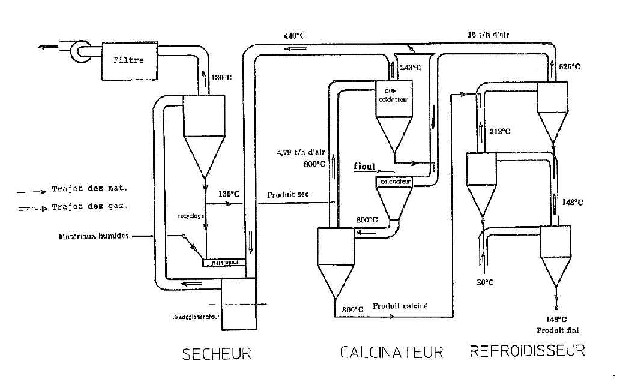
Abstract: Cement and lime are currently beeing employed as hydraulic binders to stabilize soils that make up tracks or under layers of a road. Our work has been to design a mobile installation that turns natural clay soils into synthetic pozzolana that will replace cement, by drying, grinding and calcining them. In the first instance, we selected industrial processes based upon "suspension" or "flash" heat exchanges. Flash calcination parameters (temperature, duration) are lacking in the literature. Bibliographic results obtained by traditionnal calcination (10 minutes duration at least) nevertheless enabled us to establish a thermo-chemical model simulating the transformation. When used for flash calcination (a matter of seconds), the model gave results which we compared with experimental values from a laboratory flash calciner built for the purpose, and from an existing pilot. Mineralogical and structural properties of flash calcined products have been studied; two lime reactivity tests enable us to assess the binders we obtained, and to optimise flash calcination temperatures. Two kaolinite type clays, a montmorillonite and a natural soil have been processed. From this study, we have established the thermal balance of an industrial installation, and we give a conceptual sketch for the calciner and the cooler.
DEA work of O. Pons
Conception et dimensionnement d'une installation de séchage/calcination flash de minéraux.
September 1992, Laboratoire de Mécanique, INSA de Toulouse.
A 800 kg/h production pilot-unit was constructed and operated in 1995.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publications
A comparison of the kinetics of flash calcination of kaolinite in different calciners.
Meinhold R.H., Salvador S., Davies T.W., Slade R.C.T .
Trans. IChemE, Vol. 72, Part A, January 1994, 105-113.
Modelling of combined heating and dehydroxylation of kaolinite particles during flash calcination; production of metakaolin.
Salvador S., Davies T.W.
Processing of Advanced Materials, 9, 1994, 128-135.
Pozzolanic properties of flash calcined kaolinite: a comparative study with soak calcined products.
Salvador S.
Cement and Concrete Research, 1995, Vol. 25, N°1, 102-112.
Dehydroxylation sequences of gibbsite and boehmite: study of differences between soak and flash calcination and of particle size effects.
Ingram-Jones V.J., Slade R.C.T., Davies T.W., Southern J.C., Salvador S.
J. Mater. Chem., 1996, 6 (1), 73-79.
A semi-mobile flash dryer-calciner unit to manufacture pozzolana from raw clay soils.
Salvador S., Pons O.
Construction and Building Materials, 14 (2000) 109-117.
Congress
Les propriétés des métakaolins obtenus par calcination en lit fixe et par calcination flash.
Salvador S., Cappelin I.
Bulletin de Liaison de la Société de Minéralogie et de Cristallographie, 1992, Vol. 4/2.
Présenté aux journées d'Orléans, 7-9 sept. 1992.
Prototyping flash calciners for the manufacture of synthetic pozzolana from kaolinite clay.
Salvador S.
Flash Reaction Processes, T.W. Davies (ed.), 1995 Kluver Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. NATO ASI Series, Series E: Applied Science - Vol. 282, pp 295-318.
Patent
« Installation de traitement thermique de matières pulvérulentes en suspension, et application pour la calcination flash de matières minérales notamment argileuses ».
Raynaud G., Pons O., Valmalette P., Salvador S.
Brevet déposé le 5 Juin 1997, en France, N° 97.06971, par Entreprise MALET.
Extension : International Patent PCT / FR98 / 01149 - Publication No. WO98 / 55418.